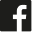Beijing, National Bank
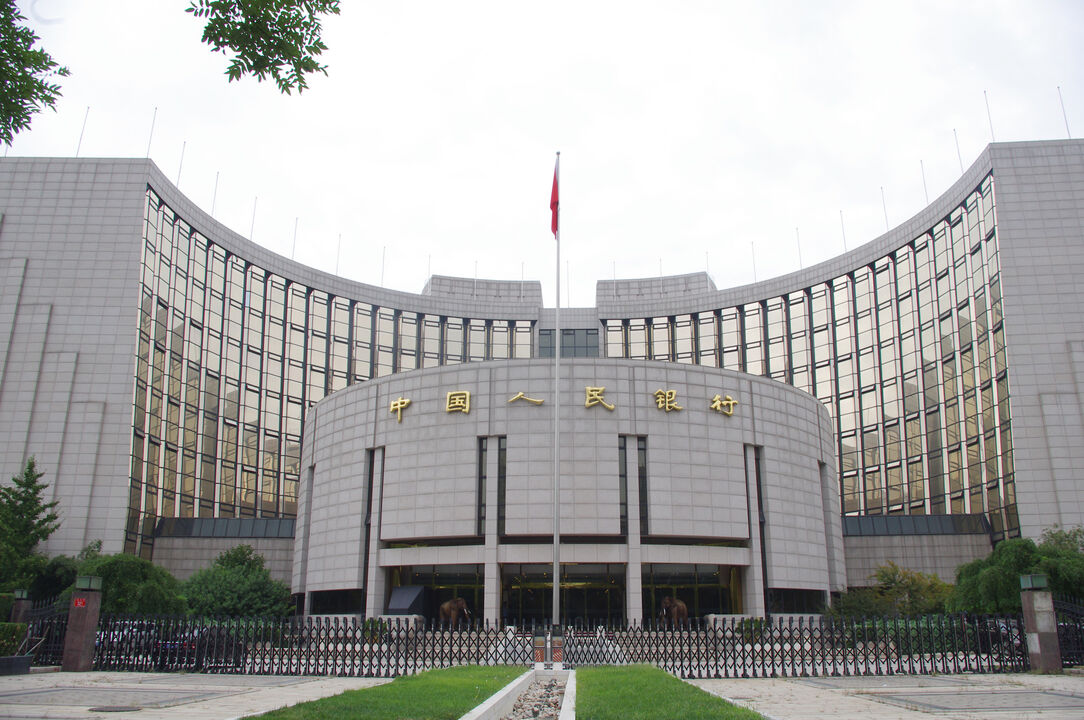
The People's Bank of China (PBC or PBOC) is the central bank of the People's Republic of China with the authority to carry out monetary policy and regulate financial institutions in mainland China. The bank was established on December 1, 1948 and today it has more financial assets than any other public institution, and is second only to the Federal Reserve System of the United States in terms of overall central bank assets. The headquarters was first located in Shijiazhuang, Hebei, and then moved to Beijing in 1949. Since March 18, 1995 the People's Bank of China legally functions as the central bank of China and is now the largest central bank at US$3.201 trillion. The PBC has established 9 regional branches and 6 overseas representative offices in London, Frankfurt, Tokyo and the Caribbean as well as for America and Africa.